Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common form of cancer and the most common form of skin cancer. The Skin Cancer Foundation cites an estimated 3.6 million cases of basal cell carcinoma diagnosed in the U.S. each year.
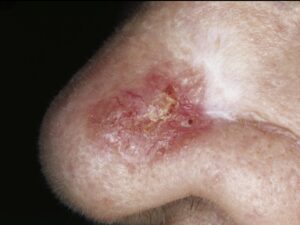
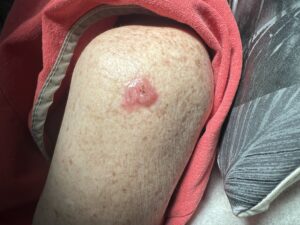
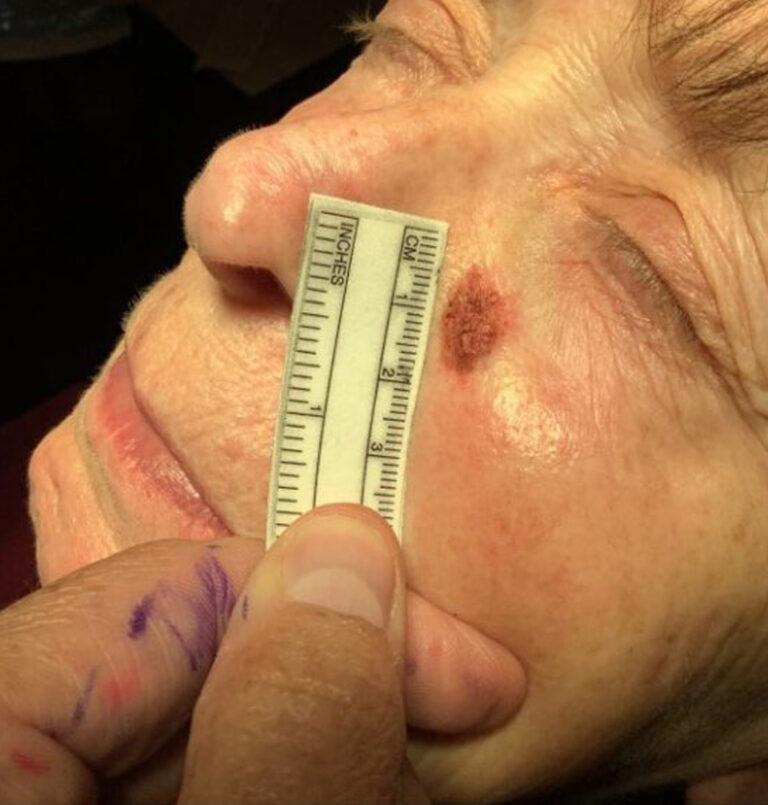
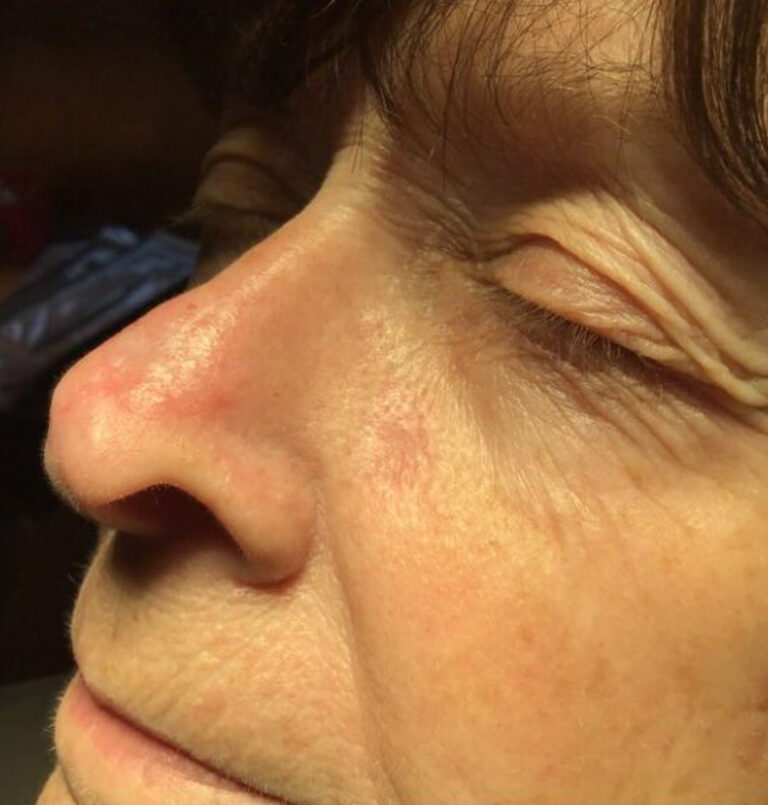
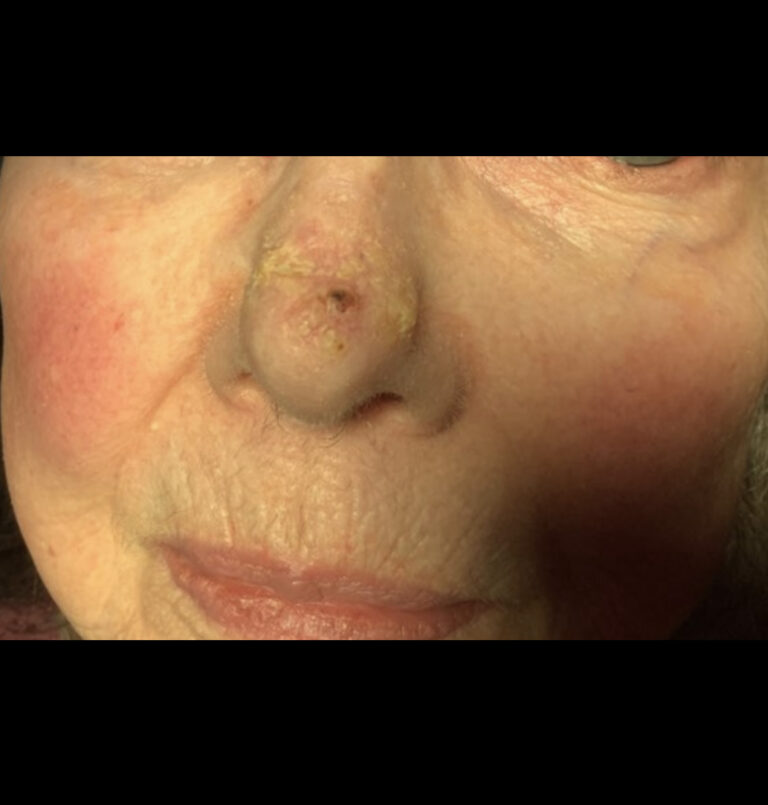
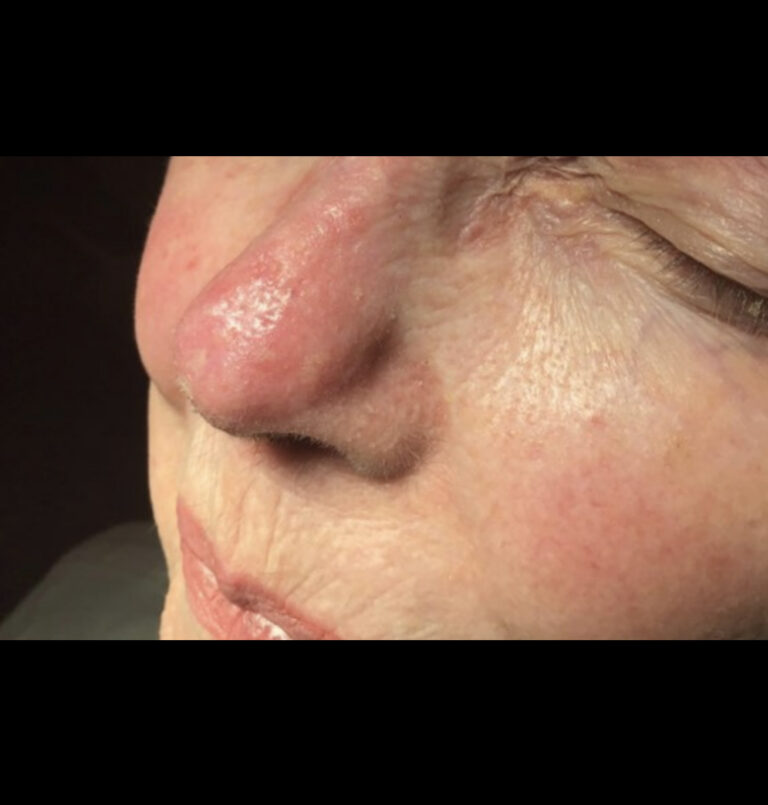
Basal cell carcinoma often appears as a slightly transparent or pink bump or patch on your skin, though it may take other forms. It’s usually found on areas on the body damaged by ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or tanning beds. All skin types can develop basal cell carcinoma, however, people with light skin that rarely tan and tend to freckle, red or blond hair and light-colored eyes have a greater risk of developing it.
Before basal cell carcinoma develops, people with lighter skin tones often notice signs of sun damage on their skin, such as age spots, patches or discolored skin and deep wrinkles. A slowly growing, non-healing spot that sometimes bleeds can also be a sign of basal cell carcinoma. Early detection is key as most basal cell carcinomas can be treated and cured if treated promptly.