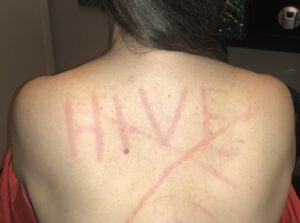 Hives are bumps that can pop up on your skin when you’ve been exposed to something you’re allergic to or that bothers your body. Your own sweat, cold, sunlight or the light pressure of a purse strap can cause hives; this is called inducible hives. It only develops when something that causes hives for you touches the skin.
Hives are bumps that can pop up on your skin when you’ve been exposed to something you’re allergic to or that bothers your body. Your own sweat, cold, sunlight or the light pressure of a purse strap can cause hives; this is called inducible hives. It only develops when something that causes hives for you touches the skin.
Most hives are very itchy; they can be as small as a pinhead or several inches across. They may appear alone or in a group, and some join together to form large patches called plaques. They’re usually harmless and temporary. A single hive can last anywhere from a few minutes to a few hours; most clear within 24 hours. If new hives continue to appear for six weeks or longer, you likely have a condition called chronic inducible hives.
Some people develop swelling deep in their skin or the moist tissue that lines the mouth/lip, eyelids or other areas. This is called angioedema and is usually harmless. Yet it can be life-threatening if it causes swelling in your mouth or throat, problems breathing or racing heart.
If you notice rapidly appearing and disappearing red or skin-colored bumps on your skin, it is unlikely to be bug bites. Instead, this could be a case of hives, which are itchy, raised, red dots or welts that can appear on the skin. Hives can be triggered by various substances and situations, often starting as an itchy patch of skin. If you suspect you have hives or any other skin condition, the dermatologists at The Art of Skin Dermatology can provide assistance. Our practice offers comprehensive treatments for a wide range of skin conditions, including hives and chronic hives. To schedule an appointment and learn more about the skin conditions we treat, please contact the dermatologists at The Art of Dermatology today.
What Are Hives?
Hives, also referred to as urticaria, welts, weals, or nettle rash, manifest as itchy, raised, red bumps or patches on the skin’s surface. These irritating marks can be triggered by an allergen or a substance that causes an allergic response. The size of hives can vary greatly, ranging from tiny welts resembling the tip of a pen to larger splotches resembling a dinner plate. Sometimes, these welts may merge together, forming even larger plaques. When the welts occur deeper beneath the skin, it is known as angioedema, which can happen alongside hives. Hive welts can emerge on any part of the body covered in skin. They may appear and disappear repeatedly as the reaction progresses. Hives can be red, pink, or flesh-colored and may cause a stinging or painful sensation. In most cases, hives are a temporary issue that can be managed with various allergy medications and will resolve on their own. However, chronic hives and hives accompanied by a severe allergic reaction are serious medical concerns that require immediate attention from a healthcare professional.
What Causes Hives?
Hives are a common condition that can affect anyone at any time. One of the main causes of hives is an allergic reaction to something you have come into contact with or ingested. When your body experiences an allergic reaction, it releases histamines into your bloodstream. Histamines are chemicals produced by the body to defend against potential threats like infections. However, in some individuals, histamines can cause symptoms such as swelling, itching, and redness of the skin, among other common hives symptoms. Allergic reactions to various triggers can lead to hives, including pollen, medications, certain foods, animal dander, dust mites, plants, and insect bites or stings. In addition to allergies, hives can also be triggered by stress, with extreme feelings of stress leading to stress hives. Excessive exposure to heat can cause heat hives, while hives can also occur due to exercise, illnesses, or infections. Prolonged exposure to hot or cold temperatures or irritation from excessive sweating can also result in hives. Hives can also be idiopathic (unknown cause ) . With so many potential triggers, it can be challenging to pinpoint the exact cause of a hives outbreak.
It is important to note that hives can vary in severity and duration. Acute hives typically last for a short period and can be managed with over-the-counter antihistamines or other allergy medications. However, chronic hives, which persist for more than six weeks, require medical attention to identify and address the underlying cause. In some cases, hives may be accompanied by a severe allergic reaction known as angioedema, which can cause swelling in deeper layers of the skin and mucous membranes. This type of reaction requires immediate medical attention.
If you experience hives or suspect you have an allergic reaction, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist. They can help determine the cause of your hives and recommend appropriate treatment options to alleviate symptoms and prevent future outbreaks.
What Do Hives Look Like?
Hives can manifest in various forms on the skin, ranging from small to large, and can take on different shapes. They may appear as ring-shaped or oval welts, or they can have more irregular and non-circular shapes. In many cases, hives can resemble insect bites, such as mosquito bites. They can be red and inflamed, with a red halo surrounding them. However, hives can also present as smooth, raised bumps or markings on the skin that are flesh-colored. When pressed with a finger, these markings may temporarily turn pale or white before returning to their original color. Hives can change in size, merge together to form larger plaques, appear in clusters or batches, spread to other areas of the body, and even undergo changes in shape and color.
During a hive flare-up, individuals may experience stinging, itching, or burning sensations. The affected areas can swell, disappear, and then reappear within a short period of time or as the reaction progresses. These flare-ups can occur multiple times in a day or persist for weeks or even months. While hives can appear on any part of the body, they are most commonly found on the face, neck, arms, hands, fingers, legs, feet, and toes. However, individuals with chronic hives may face disruptions to their daily routines, such as difficulty sleeping comfortably. They may also experience severe symptoms, including swelling of the lips, eyelids, tongue, and throat. This swelling may or may not be symmetrical and can cause significant pain and a burning sensation.
Hives Symptoms
Individuals with known allergies are at a higher risk of developing hives compared to those without allergies. This includes individuals who are on medications or may unknowingly come into contact with substances they are allergic to. People who are already ill or have pre-existing infections or health conditions may also be more susceptible to hives. Hives can occur anywhere on the body.
It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you develop hives around your tongue or throat or experience difficulty breathing, as this can be a sign of a severe allergic reaction.
The common signs of hives include slightly raised, pink, red, or flesh-colored welts, bumps, or swellings. These welts can appear individually or in groups and may cover a large area of the body. Hives can also appear and disappear quickly, reappearing on the same or different parts of the body. They can be itchy, swollen, and may sting or burn. The bumps can be small and round, ring-shaped, or large and have a random shape. Additionally, hives can grow larger, change shape, and spread to other parts of the body. If you experience these symptoms, it is advisable to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Hives Vs. Rash
Hives and skin rashes may share some similarities in terms of their appearance and symptoms, but they are distinct conditions. Hives are a specific type of rash characterized by swollen, red, pink, or skin-colored bumps on the skin that appear and disappear rapidly. When pressed, hives tend to turn white temporarily. Both hives and other rashes can cause inflammation, discomfort, and itching. In some cases, hives may produce a sensation of heat on the skin, similar to a heat rash (miliaria), which can be caused by excessive exposure to hot and humid weather. While hives and psoriasis may share certain characteristics, they are different conditions. Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disorder characterized by the rapid accumulation of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick skin plaques and lesions. In contrast, hives typically present as raised, smooth bumps that appear suddenly and can disappear just as quickly. It is important to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for any skin condition.
Types Of Hives
There are different types of hives, including acute hives, chronic hives, and physical hives.
- Acute Hives: Acute hives are characterized by hives or swelling that occur and last for less than six weeks at a time. They typically come on suddenly and are often caused by an allergic reaction to certain foods, medications, or other substances.
- Chronic Hives: Chronic hives are characterized by hives that persist for more than six weeks. In most cases, the exact cause of chronic hives is unknown, although it is believed to be related to an autoimmune response.
- Physical Hives: Some individuals may develop hives in specific situations. For example, exposure to cold, heat, or sunlight can trigger hives on the skin. Hives can also be caused by vibrations, pressure, exercise, or sweating. These physical hives typically appear within an hour after exposure.
It is important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of hives and to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
