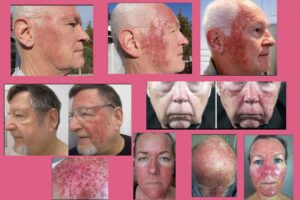
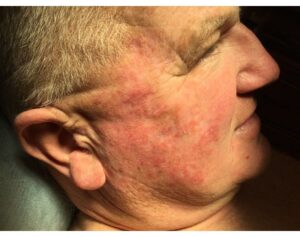
 Actinic Keratosis (AK), also called solar keratosis, is one of the most commonly diagnosed and treated conditions. AK is a precancerous skin growth caused by the sun or indoor tanning. It often appears as a reddish, rough, scaly patch or spot that develops on skin that wasn’t protected from the sun over years—commonly on your face, lips, ears, back of your hands, forearms, scalp or neck.
Actinic Keratosis (AK), also called solar keratosis, is one of the most commonly diagnosed and treated conditions. AK is a precancerous skin growth caused by the sun or indoor tanning. It often appears as a reddish, rough, scaly patch or spot that develops on skin that wasn’t protected from the sun over years—commonly on your face, lips, ears, back of your hands, forearms, scalp or neck.
More specifically, AKs are skin lesions that typically develop on the most exposed areas of the body and are considered an early warning sign of squamous cell carcinoma, the second most common form of skin cancer. According to the American Skin Association, “They appear as 1-4 mm red to brown spots that do not go away. They often have a rough and gritty texture and are often easier felt than seen. The skin surrounding the spots might appear red and irritated. These spots may sting, itch or bleed upon scratching. One cannot predict which AKs progress to squamous cell carcinoma, but lesions on the lips and ears have a higher likelihood of progression.”