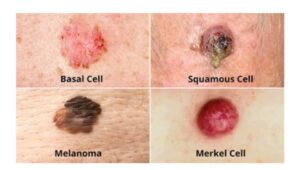
 One in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the U.S.. Fortunately, it’s also one of the most preventable cancers and can be treated successfully when found early.
One in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the U.S.. Fortunately, it’s also one of the most preventable cancers and can be treated successfully when found early.
