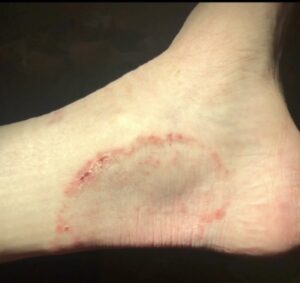
 Treatment for Ringworm
Treatment for Ringworm
Ringworm, also known as tinea corporis or dermatophytosis, is a highly contagious fungal infection that affects the skin or scalp. It can occur at any age and is difficult to prevent. If you suspect that you have ringworm or any other skin condition, our clinic, Gainesville Dermatology & Skin Surgery, has experienced dermatologists in Gainesville who can provide the necessary treatment. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and learn more about how we can help you with ringworm and other rashes.
Understanding Ringworm
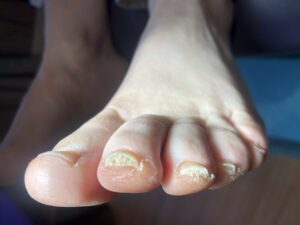
Ringworm is a rash caused by a fungal infection, despite its misleading name. The infection gets its name from the ring-shaped appearance it forms on the skin. While ringworm commonly refers to the infection on the body, it can also occur in other areas such as the scalp, groin, and feet. Early signs of ringworm include red patches on the skin that may spread to other parts of the body. It can affect various areas, including the scalp, beard, groin, feet, nails, and other body parts. Scalp ringworm, in particular, is highly contagious and presents as itchy, scaly, and bald patches on the head.
 Causes of Ringworm
Causes of Ringworm
Ringworm is caused by a contagious fungal infection that lives on the outer layer of the skin. Different types of fungi can lead to ringworm. The infection can spread through direct contact with an infected person, contact with an infected animal, contact with contaminated objects or surfaces, or even contact with infected soil. It is important to note that while ringworm can be transmitted through soil, this mode of transmission is rare and requires prolonged contact with highly infected soil.
Risk Factors for Ringworm
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of contracting ringworm. These include living in warm or humid climates, having close contact with an infected person or animal, sharing personal items with someone who has a fungal infection, participating in sports with skin-to-skin contact, wearing tight or restrictive clothing, and having a weakened immune system. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or AIDS, may find it challenging to fully treat their fungal infection.
Symptoms and Stages of Ringworm
Symptoms of ringworm vary depending on the affected area. Skin infections may present as red, itchy, or scaly patches with raised edges and a ring-like appearance. Nail infections can cause discoloration, thickening, and cracking of the nails. Scalp infections may result in hair loss and the development of bald patches. The stages of ringworm progress from an initial pink or red rash to larger, scaly, raised, and inflamed patches that are extremely itchy. Seeking treatment as soon as symptoms appear is crucial to prevent the spread and growth of the infection.
Diagnosing and Treating Ringworm
Our dermatology providers at The Art of Skin Dermatology can diagnose ringworm by examining the affected area and potentially taking samples for further testing. Over-the-counter treatments may be sufficient for mild cases, but prescription-strength antifungal medications may be necessary for more severe or extensive infections. It is essential to keep the affected area clean and dry and follow the instructions provided by your dermatologist. Untreated ringworm can lead to complications such as hair loss, scarring, and nail deformities, so seeking prompt treatment is crucial.
Contagiousness and Prevention of Ringworm
Ringworm is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated objects.
To prevent ringworm, it is important to
- Wash Your Hands After Interacting With Animals
- Disinfect And Clean Pet Living Areas
- Avoid Contact With People & Animals If Your Immune System Is Weak
- Wear Shoes If Showering Or Walking In Community Environments
- Don’t Share Personal Items, Such As Hair Brushes & Clothing, With Others
- Keep Your Skin Clean & Dry
- Keep Abrasion & Skin Injuries Covered, Clean & Dr
By following these preventive measures and seeking timely treatment, you can effectively manage and prevent the spread of ringworm. Contact The Art of Skin Dermatology to learn more about ringworm prevention and to schedule an appointment with a dermatologist.
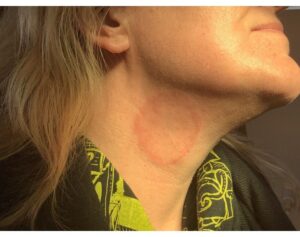 Fungal infections can occur anywhere in your body but they typically begin on your skin. Most cause some discomfort, such as redness and intense itching. Ringworm is a common skin infection caused by a fungus. The rash often has a ring-shaped pattern and a raised, scaly border. While ringworm can appear on just about any part of your body, the rash lacks the ring-shaped pattern on the palms, soles, scalp, groin and nails.
Fungal infections can occur anywhere in your body but they typically begin on your skin. Most cause some discomfort, such as redness and intense itching. Ringworm is a common skin infection caused by a fungus. The rash often has a ring-shaped pattern and a raised, scaly border. While ringworm can appear on just about any part of your body, the rash lacks the ring-shaped pattern on the palms, soles, scalp, groin and nails.
 Treatment for Ringworm
Treatment for Ringworm Causes of Ringworm
Causes of Ringworm